PLANT CELL STRUCTURE AND TISSUES:
Plant cells are the building blocks of plants and have a unique structure that allows them to carry out essential functions such as photosynthesis, respiration, and reproduction. Plant tissues, on the other hand, are groups of cells that perform specific functions in the plant body.
Here is a brief discussion on the structure of plant cells and the different types of plant tissues:
Plant cell structure:
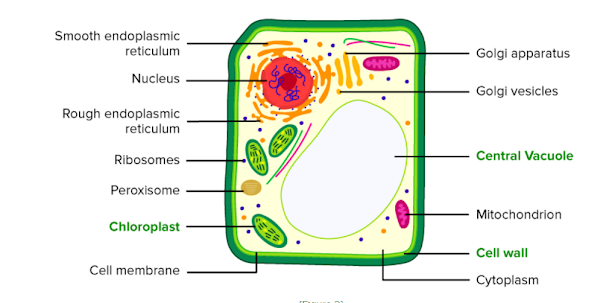
Plant cells have a cell wall made up of cellulose, which provides rigidity and support to the cell. The cell membrane lies inside the cell wall and regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. Plant cells also contain several organelles, such as the nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and vacuoles.
The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the genetic material. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis and contain chlorophyll. Mitochondria are involved in respiration and provide energy to the cell. The Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum are involved in protein synthesis and transport. Vacuoles are storage structures that store water, minerals, and waste products.
Plant tissues:
Plant tissues are broadly classified into two types: Meristematic tissue and Permanent tissue.
a) Meristematic tissue:
These are actively dividing cells that are responsible for growth and development in plants. They are found in the tips of roots and shoots, where they produce new cells that differentiate into various types of permanent tissues.
b) Permanent tissue:These tissues are derived from meristematic tissue and have lost their ability to divide. They can be further classified into three types:
1. Epidermal tissue:
This tissue covers the outer surface of the plant and protects it from water loss, pathogens, and other environmental factors.
2. Ground tissue:
This tissue is responsible for various functions such as photosynthesis, storage, and support. It is found between the epidermis and the vascular tissue.
3. Vascular tissue:
This tissue is responsible for the transport of water, nutrients, and other materials throughout the plant. It is further divided into two types: Xylem and Phloem. Xylem tissue transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves, while Phloem tissue transports food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant.
In conclusion, the plant cell structure and tissues play a vital role in the growth, development, and survival of plants. Understanding these structures and their functions is essential for students pursuing Botany or any other plant-related fields.


Comments
Post a Comment